
The purpose of Graduate Medical Education (GME) is to provide an organized educational program with guidance and supervision of the resident/fellow, facilitating the resident/fellow's ethical, professional, and personal development while ensuring safe and appropriate care for patients. LMU-DCOM fully supports the mission of the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) “to improve health care and population health by assessing and advancing the quality of resident physicians' education through accreditation.” LMU-DCOM accomplishes this through partnerships with institutional sponsors of GME. LMU-DCOM also possesses the structure and ability to become an institutional sponsor, should the need arise.
LMU-DCOM has an ongoing plan to assist affiliated residency and/or fellowship programs to achieve Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) requirements for Osteopathic Recognition. This will be accomplished through the efforts of the GMEC, which will provide the support and resources needed to allow for effective delivery of shared services to all of our affiliated ACGME accredited programs. An OPP Subcommittee will assist in this endeavor through responsibilities including planning, developing, implementing, and evaluating the integration, not only of OPP in the curriculum and patient care for the COM, but also to provide expertise to affiliated ACGME programs relating to the ACGME Osteopathic Recognition standards. Oversight of this will occur through combined efforts of the departments of GME, Clinical Education, and OPP while also utilizing faculty and resources in other areas. For more information, please access the policy link below:
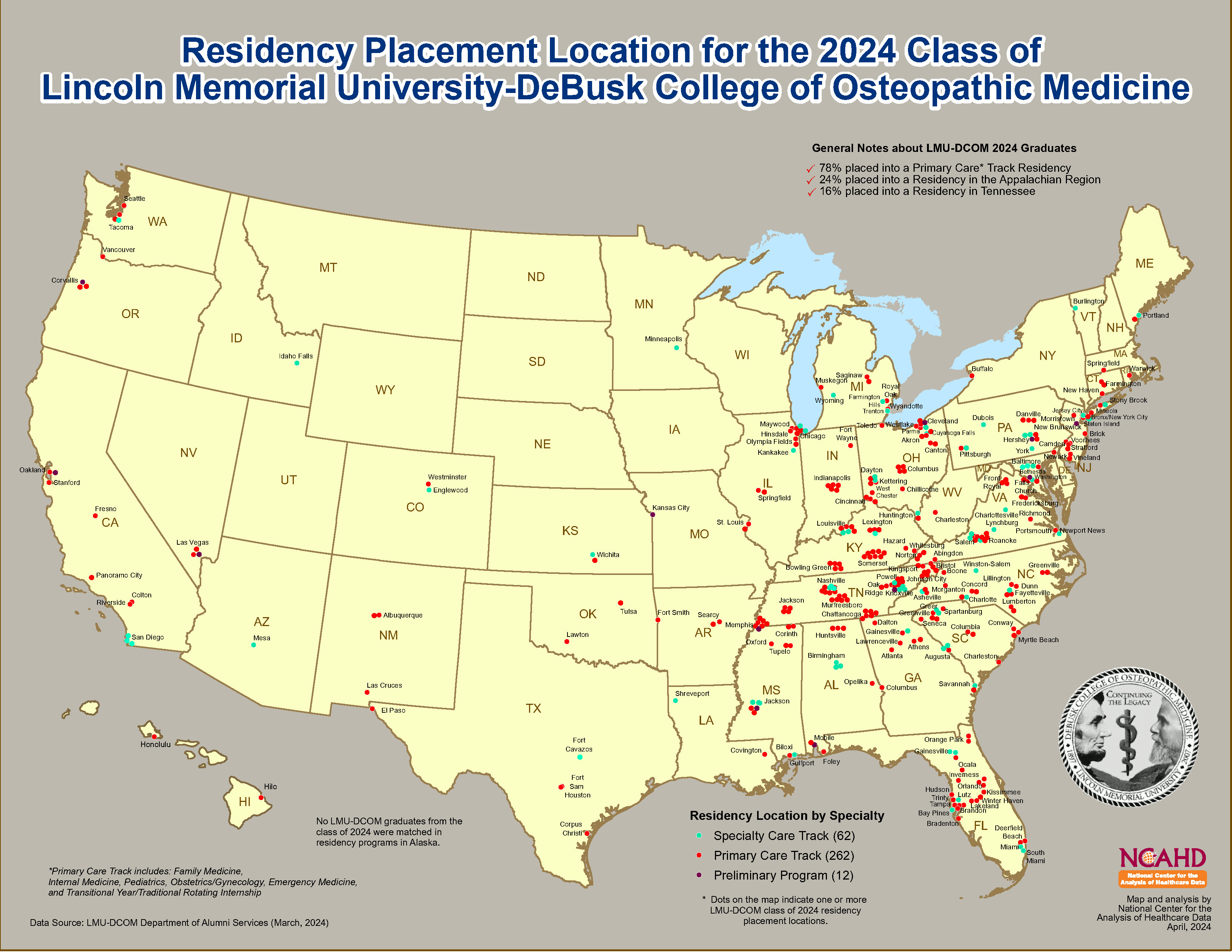
LMU-DCOM Policy 10.1-10.2 (Graduate Medical Education)
Continuing Medical Education (CME) consists of educational activities which serve to maintain, develop or increase the knowledge, skills and professional performance and relationships that a physician uses to provide services for patients, the public or the profession. The content of CME is that body of knowledge and skills generally recognized and accepted by the profession as within the basic medical sciences, the discipline of clinical medicine and the provision of health care to the public.
In June 1973, The American Osteopathic Association (AOA) established a continuing medical education (CME) program requirement for physicians who wish to maintain their Association membership. The purpose of the AOA's continuing medical education program is to continually improve the quality of patient care, through the growth of knowledge, the improvement of skills, and physician-to-physician interaction.
As an AOA CME Sponsor, LMU-DCOM will strive to foster exemplary continuing medical education practices in meeting the teaching and learning needs of its faculty and community-based preceptors, committed to its mission of life-long learning, and addressing the changing landscape of health care.
The American Heritage Dictionary online defines "preceptor" as 1. A teacher; an instructor; 2. An expert or specialist, such as a physician, who gives practical experience and training to a student, especially of medicine or nursing; 3. The head of a preceptory.
Chickerella and Lutz (1991) define preceptorship as "An individual teaching /learning method in which each student is assigned to a particular preceptor...so that she can experience day-to-day practice with a role model and resource person."
Faculty development refers to those programs which focus on the individual faculty member. The most common focus for programs of this type is the faculty member as teacher. Faculty development specialists provide consultation on teaching, including class organization, evaluation of students, in-class presentation skills, questioning and all aspects of design and presentation. They also advise faculty on other aspects of teacher/student interaction, such as advising, tutoring, discipline policies and administration.
A second frequent focus of such programs is the faculty member as a scholar and professional. These programs offer assistance in career planning, professional development in scholarly skills such as grant writing, publishing, committee work, administrative work, supervisory skills and a wide range of other activities expected of faculty.
A third area in which faculty development programs focus is the faculty member as a person. This includes wellness management, interpersonal skills, stress and time management, assertiveness development and a host of other programs which address the individual's well-being.
While not all faculty development programs include all these areas, most of them have as their philosophy the faculty member as the driving force behind the institution; therefore, assisting that person to be as productive as possible will make the entire institution more productive.